Railway Testing
Beyond Boundaries, Beyond Flaws: Scan Scope Technologies Redefining NDT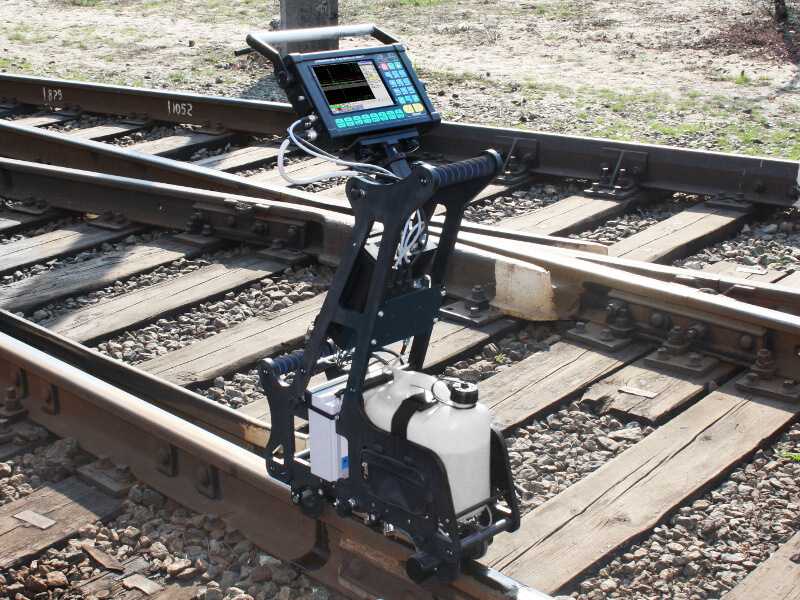


Ultrasonic Testing
Railway tracks are inspected by ultrasonic high frequency waves. Usually ultrasonic rail flaw detector uses the ultrasonic waves with a frequency of 2 to 5 MHz to inspect rails.
The defects in rails have different nature: direction of development, manufacturing defects, operational defects. That’s why manufacturers of the ultrasound testing equipment create railway crack detectors with various sounding schemes and types of probes. Different angles of ultrasound input into the rail and testing methods (echo method, echo-shadow method, tandem method) are used as well.
Besides that, the manufacturers of the ultrasonic rail testers and the ultrasonic weld testing equipment implement different types of data output to the screen, for example: A-scan, B-scan and their various combinations for the efficient defects detention.
The variety of testing methods and sounding schemes, as well as various types of data visualization make it possible for the ultrasonic testers to detect the defects effectively and with great probability at different stages of their development.
Eddy current railroad track inspection tools
In the rails head acting surface, as well as on the rail head running surface the quenching cracks may be developed in the process of the rails exploitation.
This type of defect initially appears on the rail surface and develops to the depth after some time.
Eddy current rail inspection equipment is highly efficient for detecting this type of defects. Timely detected and assessed defect depth in the rail head and on the head running surface allows to extend the service resource by the rail profile recovery with the grinding machines.
In this case the application of eddy current railroad track inspection tools is justified not only by a possibility to detect flaws but also by their assessment.
Mechanized ultrasonic rail flaw detectors allow:
- to carry out continuous monitoring at a speed of up to 4 km/h for defects in both rails of the railway track along the entire length and section of it, with the exception of the flanges of rail foot;
- to fulfill manual confirming testing of individual sections of rails and welds;
- to determine the parameters of detected defects and store the results of testing in energy-independent memory.
Manual testing equipment of rails and welded rail joints
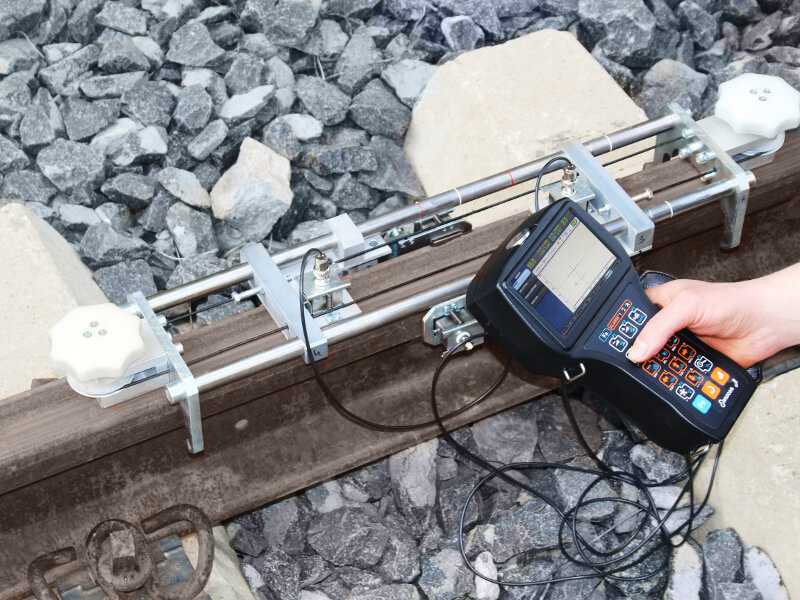
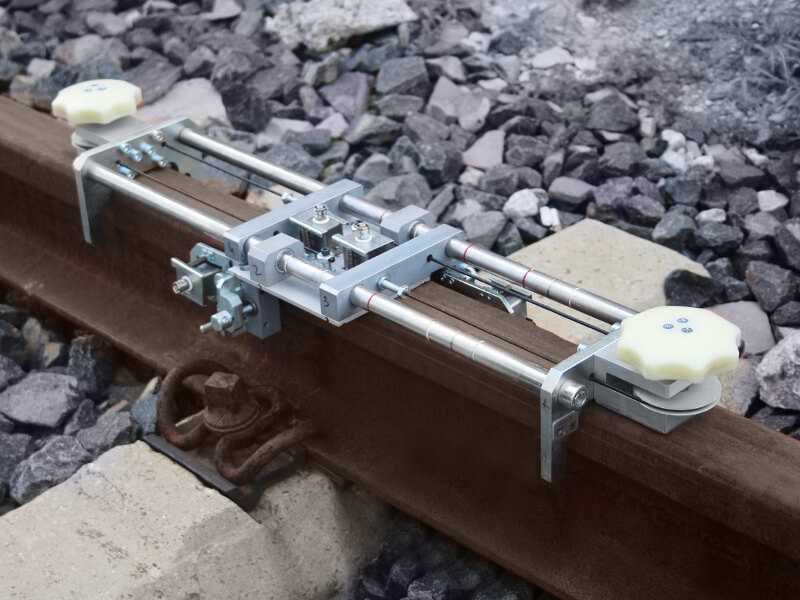

At the moment various rail testing equipment is used in ultrasonic rail inspection, which in turn require the participation of a person to interpret the results of their test.
Different regions and countries prefer to use different types of ultrasonic rail flaw detectors.
Manual ultrasonic inspection of rails implies using hand-held ultrasound testing equipment, such as portable UT flaw detector Sonocon B plus a set of ultrasonic transducers and a special scanning device (USR-01).
Combined application of manual UT rail flaw detector and ultrasonic weld inspection equipment allows to carry out a secondary testing of railroad tracks laid, according to the results of mechanized inspection by ultrasonic railways crack detectors or trolleys.
Also, the above mentioned rail inspection equipment allows to fulfill the pre-weld inspection of the end sections of new and used rails before welding them at rail welding enterprises or monitoring joints welded by electrocontact or aluminothermic methods.
This technology lies in the fact that the ultrasonic testing of railway tracks is carried out by means of high-speed transport systems (vehicle, wagon or rail car) without stopping along the assigned route; this allows you to inspect areas exceeding 100 km per shift.
After that, the monitoring data is sent and analyzed in a remote location. Once the data has been analyzed and potentially dangerous sections of rail are revealed, the report is sent to the operators who are conducting confirmatory checks with the help of manual or mechanized flaw detectors.
